What Are The Important Recruitment Metrics?
Organizations must leverage data-driven insights to optimize their recruitment strategies in today’s competitive job market. Recruitment metrics play a crucial role in measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of the hiring process. This article will explore key recruitment metrics, including Time to Fill, Time to Hire, Cost per Hire, Vacancy Cost/Impact, Sourcing, and Retention Rates. Understanding and analyzing these metrics can help organizations make informed decisions, improve recruitment outcomes, and drive business success.
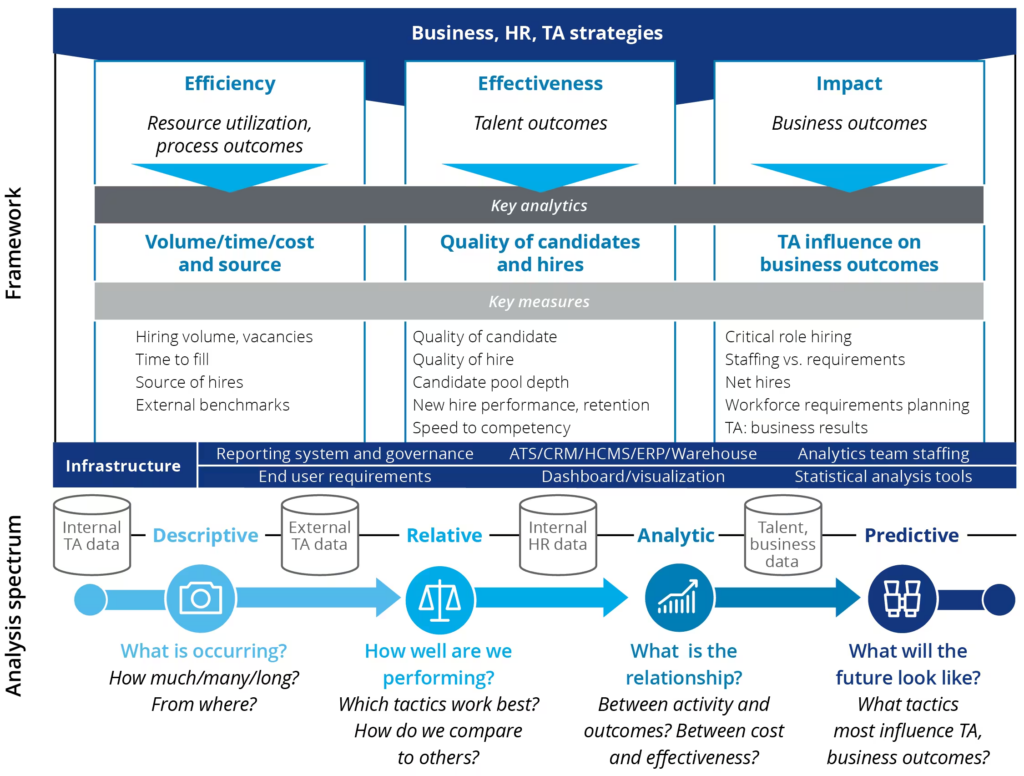
Recruitment Metrics
Time to Fill (TtF) and Time to Hire (TtH)
Time to Fill and Time to Hire are critical metrics that measure different stages of the recruitment process. First, let’s distinguish between Time to Hire and Time to Fill and how to measure them. Time to Fill measures the duration between creating a job opening and successfully filling the position and reflects an organization’s efficiency in promptly replacing or adding new members to the workforce. Time to Hire, on the other hand, measures the time taken from a candidate’s entry into the recruitment process to their acceptance of the job offer. It assesses the efficiency of the hiring process in attracting and securing top talent.
Analyzing these Talent Acquisition Metrics helps organizations identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and reduce delays in recruitment, ultimately enhancing workforce productivity and minimizing the impact of vacant positions. Generally, organizations measure Time to Fill and Time to Hire metrics as often as weekly or biweekly. This is important to keep talent acquisition efforts adaptive to the ever-changing job market.
Cost per Hire (CPH)
Cost per Hire is a crucial financial metric in recruitment that calculates the expenses incurred throughout the hiring process. It encompasses various components such as advertising costs, agency fees, background checks, candidate travel expenses, candidate marketing expenses, interview expenses, vacancy-related costs, and candidate sourcing expenses.
Tracking and analyzing Cost per Hire empowers organizations to assess the efficiency of their recruitment budget allocation, identify potential cost-saving opportunities, and maximize the return on investment (ROI) in talent acquisition. By optimizing recruitment expenses, including candidate sourcing expenses, interview expenses, and vacancy-related costs, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and achieve greater cost-efficiency in their hiring efforts. This enables them to make strategic decisions, improve overall recruitment ROI, and attract top talent to grow their business. Generally, organizations track Cost per Hire (CpH) metrics quarterly and benchmark them against annual or bi-annual measurements.
Vacancy Cost & Impact
Vacancy Cost/Impact is a powerful metric that quantifies the financial impact of a vacant position on an organization. It takes into account factors such as lost productivity, decreased customer satisfaction, increased workload on existing employees, missed business opportunities, incidental replacement costs, recruitment budgeting, agency justification, succession planning, growth planning, impact on revenue, production, and growth, coverage or locum expenses, vacancy length, and time to peak performance during onboarding and training.
By tracking the incidental replacement costs of a vacancy or delayed growth cost, organizations comprehensively understand the financial implications of delayed hiring decisions. This metric serves as a reminder of the importance of reducing Time to Fill and Time to Hire, emphasizing the negative consequences of prolonged vacancies on overall business performance. It also helps organizations in recruitment budgeting, justifying the need for agency support, succession planning, and growth planning. Furthermore, by quantifying the impact of a vacancy, organizations can make informed decisions to mitigate the financial repercussions, optimize resources, and ensure a smooth transition when filling the position.
Vacancy cost is a vital metric that organizations typically measure annually or bi-annually, as it plays a significant role in talent acquisition department budgeting. This metric holds importance for multiple stakeholders, including human resources, talent acquisition, operations, and hiring teams.
Tracking and analyzing vacancy costs allows organizations to understand the financial impact of unfilled positions on their operations and overall budget. By quantifying the cost of vacancies, organizations can effectively allocate resources, plan for hiring needs, and make informed decisions to minimize the negative consequences of prolonged vacancies. This metric is a valuable tool for stakeholders involved in talent acquisition and ensures a proactive approach to managing vacancies and optimizing organizational performance.
Candidate Sourcing
Sourcing metrics are critical in assessing the effectiveness of various marketing channels and candidate sourcing strategies to attract qualified job applicants. These metrics encompass factors such as the number of applicants, the quality of applicants, and the conversion rate from applicant to hire.
Analyzing sourcing metrics enables organizations to determine the most efficient sourcing and outreach mediums to maximize return on investment (ROI). Metrics like Source Success Ratio, Marketing ROI, Source Retention rates, Time to Source, Candidate Hire Source, Employer branding budgeting, and measurements conducted quarterly provide insights into the success of different sourcing channels. Stakeholders such as talent acquisition teams, human resources, hiring managers, and organizational leaders are interested in these metrics as they allow for data-driven decision-making, improved budget allocation, and enhanced recruitment strategies.
By leveraging candidate sourcing metrics, organizations can identify the most effective channels for reaching their target audience, whether it be job boards, social media platforms, industry-specific networks, or employee referrals. This knowledge helps optimize sourcing efforts, improve the candidate pool’s quality, and ultimately reduce the Time to Fill. Stakeholders are vested in these metrics as they enable them to make informed decisions, maximize their recruitment budget, and attract top talent efficiently and cost-effectively.
Retention Rates
Retention rates are a critical metric that measures an organization’s ability to retain employees over a specific period. This metric provides valuable insights into employee satisfaction, engagement, and the effectiveness of talent management strategies.
Analyzing retention rates enables organizations to identify areas for improvement in their onboarding processes, training programs, career development opportunities, and overall employee experience. Stakeholders, including human resources, talent acquisition, managers, and organizational leaders, are interested in this metric as it facilitates succession planning, interventions to improve retention, engagement, and satisfaction, evaluation of employee longevity, justification for employee exits, assessment of counteroffer costs, and measurement of vacancy costs.
To effectively track and analyze retention rates, it is common to conduct regular check-ins, such as 2 to 2.5-year retention check-ins and 30, 60, and 90-day onboarding check-ins. Additionally, quarterly analysis helps identify trends and patterns in retention rates, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions to enhance employee retention.
High retention rates have numerous benefits for organizations. They reduce the need for frequent hiring, saving recruitment costs and maintaining workforce stability. Moreover, high retention rates contribute to a positive employer brand reputation, attracting top talent and creating a work environment that fosters loyalty and commitment.
Overall, retention rates are a crucial metric for stakeholders as they provide insights into employee longevity, help guide intervention strategies, inform succession planning, and support effective talent management practices. By monitoring and improving retention rates, organizations can create a positive work culture, enhance employee satisfaction, and achieve long-term success.
Considering Recruitment Data Sources
When it comes to reporting on talent acquisition (TA) data, leading companies have evolved beyond relying solely on their applicant tracking system (ATS). With the implementation of advanced systems, data repositories, and analytics capabilities, organizations can access a broader range of integrated insights regarding the impact of TA processes and practices. This expanded aperture includes data from various sources, such as:
- Core HR, talent, learning, performance management, and compensation systems: These systems provide valuable information about new hires and high performers, including their demographic details and how they influence talent outcomes.
- Skills inventories: Organizations utilize skills inventories to identify any surpluses or shortfalls in skills within specific roles and geographies, enabling them to address skill gaps effectively.
- Candidate relationship management (CRM) systems: CRM systems offer insights into talent pools, helping organizations understand and engage with passive candidates while gaining a deeper understanding of their employment brand strength.
- Social networks: By leveraging social networks, organizations can gather valuable insights about passive candidates and assess the strength of their employment brand, which contributes to attracting top talent.
- Employee engagement surveys: These surveys play a crucial role in evaluating new-hire satisfaction, identifying retention risks, and assessing the success of hiring managers in creating an engaging and supportive work environment.
- Operational and financial systems: Operational and financial systems, such as sales or enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, provide critical data on recruiting costs and the impact of hiring activities on the team, business unit, and corporate results. This enables organizations to assess the financial implications of their talent acquisition efforts.
In addition to the aforementioned systems, these data sources shed light on the relative value of different sources of hire, both internal and external. Organizations can analyze the effectiveness of these sources in generating high-performing employees, fostering high levels of engagement, and identifying future leaders within specific roles, lines of business, geographies, or diversity groups.
By leveraging data from these diverse sources, organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of their talent management practices and the impact they have on various aspects of their business. This allows them to make informed decisions, drive effective recruitment strategies, and optimize their overall talent acquisition efforts for long-term success.
Summarizing Important Recruitment Metrics
Recruitment metrics provide valuable insights into the hiring process’s efficiency, effectiveness, and impact. By understanding and analyzing metrics such as Time to Fill, Time to Hire, Cost per Hire, Vacancy Cost/Impact, Sourcing, and Retention Rates, organizations can make data-driven decisions, optimize recruitment strategies, and achieve better recruitment outcomes.
Additionally, organizations should consider diverse data sources, such as core HR systems, skills inventories, candidate relationship management systems, social networks, employee engagement surveys, and operational and financial systems. These sources provide integrated insights into talent acquisition processes and the value of different sources of hire, empowering organizations to make informed decisions and optimize their talent acquisition efforts
Regularly tracking these metrics allows organizations to identify areas for improvement, reduce time-consuming delays, optimize
